Range of motion (ROM) assessments are vital in physical therapy and rehabilitation, offering insights into a patient’s joint flexibility, muscle strength, and overall functionality.
A Range of Motion (ROM) assessment typically involves a physical examination, where healthcare professionals assess the flexibility and mobility of an individual’s joints. The evaluation can be performed actively, with the patient moving the joint themselves, or passively, where the practitioner moves the joint for the patient. The angle formed by the movement of a joint, such as flexion or extension, is measured to determine the patient’s ROM. This process helps detect limitations in joint movement, which may indicate underlying issues or conditions.
There are various tools can be used to ensure precise measurements. These are:
The manual version of the instrument measures joint angles by aligning two arms with the adjacent body segments and reading the angle from the scale on the device. Goniometers are widely used due to their affordability and simplicity, but they require skill and experience to ensure accurate measurements.
Digital goniometers measure joint angles using an electronic protractor in the hinge of the two connected arms. They provide real-time, accurate measurements, improving precision and consistency in assessing a patient’s range of motion compared to manual methods.
This device is used to evaluate the flexibility and mobility of a patient’s joints by measuring the angle formed when they move a body part. Typically handheld, the inclinometer is placed on the skin near the joint being assessed. As the patient moves the body part, the device measures the change in angle. This information helps healthcare professionals understand a patient’s joint mobility, identify limitations, and develop appropriate treatment plans.
AI can be used in range of motion assessments to improve accuracy and convenience for patients and healthcare professionals alike. AI-powered solutions, such as Kemtai, use computer vision technology to track a patient’s movements through a smartphone or webcam, eliminating the need for manual measurements.
The software analyzes the movement data, calculates joint angles, and provides real-time feedback on the patient’s ROM. This not only streamlines the process but also enables remote assessments, allowing patients to perform exercises at home under virtual guidance. By incorporating AI in ROM assessments, healthcare professionals can monitor progress, tailor treatments, and improve patient outcomes more efficiently.
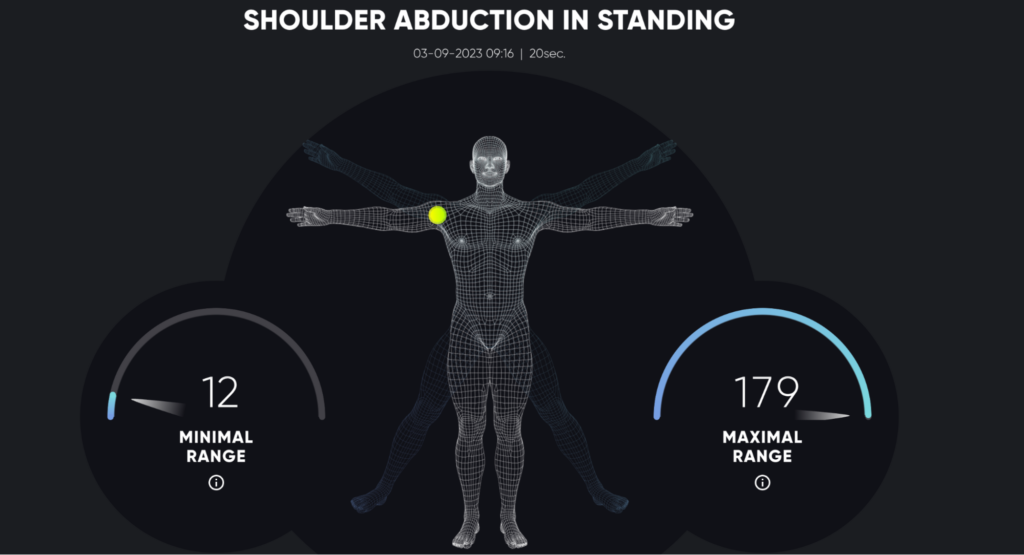
The duration of a ROM assessment using AI can vary depending on the system and the number of joints being assessed. However, AI-powered assessments are generally faster and more efficient compared to traditional methods. In many cases, an AI-based ROM assessment can take just a few minutes per joint. This is because AI systems can automatically capture, analyze, and interpret data in real-time, significantly reducing the time spent on manual measurements and calculations. What’s more, AI-powered tools allow patients to perform assessments at their own pace and in the comfort of their homes, making the overall process more time-efficient for both patients and therapists.
Healthcare professionals use different types of ROM assessments—Active Range of Motion (AROM), Passive Range of Motion (PROM), and Active-Assisted Range of Motion (AAROM)—to evaluate a patient’s joint mobility, muscle strength, and functional ability. Each type of assessment serves a specific purpose and provides unique insights into a patient’s condition:
By using different types of ROM assessments, healthcare professionals can get an understanding of a patient’s joint function, muscle strength, and limitations. This information is crucial for designing effective treatment plans and monitoring progress throughout rehabilitation.
There are several benefits to Kemtai’s innovative AI solution:
Learn more about Kemtai and its innovative technology.

ROM assessments are key in healthcare and physiotherapy, helping professionals diagnose issues, create custom treatment plans, and track progress. AI solutions like Kemtai make these assessments more efficient and user-friendly for both patients and therapists. By using advanced tech like computer vision, ROM assessments can now be done remotely with real-time feedback and precise measurements. These innovations are changing the game, improving patient results, and making life easier for healthcare experts. Embracing these changes will help boost care quality and assist patients on their path to better health and mobility.
A range of motion assessment evaluates a patient’s joint flexibility and mobility. To perform a ROM assessment, a healthcare professional guides the patient through various movements, focusing on the targeted joints. The joint angles are measured using tools like goniometers or inclinometers. AI platforms like Kemtai can assist therapists in performing ROM assessments without any handheld equipment. They leverage computer vision technology to track movements and provide real-time feedback, ultimately helping patients recover more quickly.
ROM can be assessed in two primary ways: active range of motion (AROM) and passive range of motion (PROM). AROM involves the patient moving their joint voluntarily without assistance, while PROM requires the healthcare professional to move the joint for the patient. AI solutions like Kemtai can enhance ROM assessments by accurately tracking patient movements, providing real-time feedback, and helping therapists make data-driven treatment decisions for better patient outcomes.
Documenting ROM involves recording the patient’s joint angles and any limitations observed during the assessment. Healthcare professionals use tools like goniometers or inclinometers to measure joint angles accurately. AI platforms like Kemtai can simplify documentation and data tracking by automatically capturing, analyzing, and storing assessment data. This streamlined process enables healthcare professionals to monitor patient progress more efficiently, adjust treatment plans as needed, and ultimately restore patients back to full health more speedily.