Neuromuscular re-education is a treatment technique or exercise performed with the goal of improving—via the nervous system—the level of communication between an individual’s body and brain. An example of this is training a patient post a total knee replacement surgery to improve their gait or to perform a quad set. The NMR process also includes proprioceptive training, which provides a sense of the relative position of neighboring parts in the body. The proprioceptive system provides feedback on the entire body, from its parts to their positions relative to each other. It is the sense that helps discern whether the body is moving with sufficient vigor and determines where the various body parts are in relation to each other at any given moment.
Reporting neuromuscular reeducation (NMR) is one of the more significant coding dilemmas faced by chiropractors. The many definitions and interpretations of NMR have contributed to the confusion, making reimbursement using the CPT code 97112 complex. This blog aims to clarify and describe the definition, process, documentation, and use cases linked to CPT code 97112.
What is CPT code 97112?
CPT code 97112 covers a therapeutic procedure targeting one or more areas of the body in 15 min increments where the physical therapist aims to improve function by neuromuscular reeducation of movement, balance, coordination, kinesthetic sense, posture, or proprioception.
The procedure requires direct contact with the patient and is prescribed for impairments that affect the body’s neuromuscular system, for example, poor balance while sitting or standing, loss of motor coordination, and issues with muscle tone.
The therapeutic exercises included in neuromuscular reeducation
Therapeutic exercise is defined as a physical therapy technique that is designed to improve strength and flexibility. Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF), The Feldenkrais Method, the Bobath concept, Bap’s Boards, and Desensitization are some of the techniques involved in Neuromuscular Reeducation. Let us understand each of these a bit further.
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) is a type of stretching exercise that improves flexibility and ROM. It can also be used to improve posture and balance, functional movements, and strength. PNF stretches are performed by contracting the muscle being stretched while in the stretched position. This activates sensory receptors within the muscles which send signals to the brain telling it how far to stretch before feeling pain or discomfort.
The Feldenkrais Method
The Feldenkrais Method is an organic learning process that helps a person move more easily in fundamental human movements like rolling, turning, speaking, and walking. It also affords the individual a new sense of self-confidence as he or she moves through life more easily than in the past.[1]
By incorporating both hands-on and verbally guided exercises based on sensorimotor developmental learning, the method teaches the patient to integrate feedback from both internal and external sources in order to direct his or her own movement.
Bobath’s Concept
Bobath’s Concept considers the way in which sensory input, perception of this input, and adaptive behavior affect motor problems that occur throughout a patient’s body. The treatment organizes the proprioceptive as well as the external environment of the nervous system for improving the functional efficiency of the patient. Applied mostly to patients suffering or recovering from a lesion in the central nervous system, therapy focuses on the following:
- Encouraging collaboration of the neuromuscular, nervous, and spinal cord systems to enhance function.
- Improving neuroplasticity by encouraging the interactive nervous system, and independent movement.
- Recruiting cutaneous and muscle receptors to activate the remaining intact areas of the nervous system.
Postural reeducation
Postural reeducation exercises aim to correct musculoskeletal conditions arising from bad posture. They improve balance, strength, flexibility, and coordination in the body. Treatment could include manual techniques, progressive stretches, breathing techniques, or manipulations.
EMG feedback
Electromyographic biofeedback technique uses electrodes connected to the patient’s muscles to generate a visual or auditory feedback in response to muscle movement. This allows the patient to trigger or improve function in their muscles.
Desensitizing techniques
Used for effective pain reduction, desensitization techniques involve touching and stimulation of the painful areas to gradually reduce oversensitivity. Texture rubbing, pressure, or immersion in various mediums are the most common techniques used for desensitization.
Kinesthetic training
This technique involves increasing the patient’s awareness of their own body at all times in order to perceive the extent, direction, and weight of a particular movement. The kinesthetic pathway being one of the main pathways to the brain, kinesthetic training improves a patient’s cognizance of the joint’s movements.
Apart from those discussed above, strength exercises, balance exercises, and movement reeducation are some of the other techniques used for NMR.
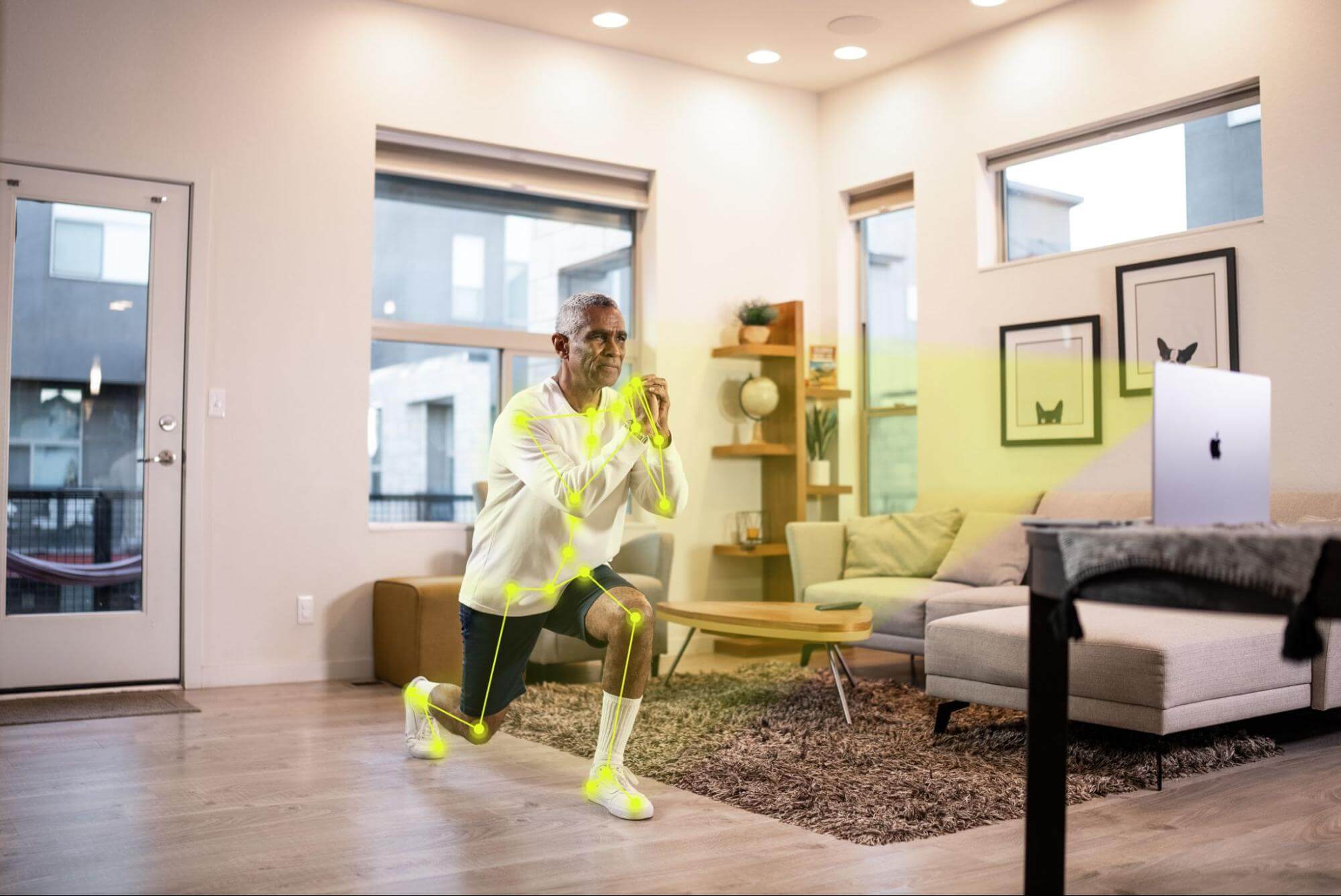
Physical therapy at home with Kemtai
Most of the techniques discussed above are done under the supervision of a trained physical therapist and exercises independently performed by the patient have to be tracked to ensure proper recovery. However, with the advent of remote therapy platforms like Kemtai, it has become simpler for the therapist to assign specific exercise routines, track the patient’s progress over time and personalize the patient’s routine. Using advanced computer vision technology to generate active adaptive feedback, Kemtai observes and corrects the patient’s movement during the exercise, and could improve the effectiveness of the exercise and could ensurie patient compliance to aid recovery.
Documentation and Coding Guidelines
97112 is a time-based code. It requires direct one-to-one contact between the patient and therapist and is billed in increments of 15 minutes. The treatment plan should be clear and specific about the clinical rationale for performing 97112. The patient’s medical history and findings from any physical examination should clearly show that the patient has impaired functional capacity with respect to posture, balance, coordination, proprioception, or specific movements. The plan of care should also specify what modalities will be applied and what specific parameters will be monitored for 97112, for example, PNF supine stretching of the left leg; balance board for 5 minutes. It is not necessary to describe the clinical approach and rationale on every visit.
Daily notes should include the anatomic site where the therapist is working, the amount of time spent on that area (e.g., PNF to bilateral hamstrings for 15 minutes), and why this is important in relation to the therapist’s evaluation and the treatment plan.
As we close…
Neuromuscular reeducation is an important component of a comprehensive treatment plan. Reeducation is the process by which the therapist teaches the patient to use muscles in a more efficient manner to avoid compensatory movements that can lead to further injury or dysfunction. Neuromuscular reeducation can be performed with very basic equipment or the most sophisticated of technologies. It is important for the therapist to understand how neuromuscular reeducation works, what it can accomplish, and when it should be used in conjunction with other treatment approaches.
References
[1] https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/nursing-and-health-professions/feldenkrais-method
[WPSM_AC id=1892]


